| 产品编号 | 产品名称 | 产品规格 | 产品等级 | 产品价格 |
| 292-62301 | Human β Amyloid(1-40) ELISA Kit Wako 人淀粉样蛋白抗体(1-40)ELISA试剂盒 |
96wells | for Immunochemistry | – |
| 298-62401 | Human β Amyloid(1-42) ELISA Kit Wako 人淀粉样蛋白抗体(1-42)ELISA试剂盒 |
96wells | for Immunochemistry | – |
| 296-64401 | Human β Amyloid(1-42) ELISA Kit Wako, High Sensitive 人淀粉样蛋白抗体(1-42)高灵敏度ELISA试剂盒 |
96wells | for Immunochemistry | – |
| 298-64601 | Human β Amyloid(1-40)ELISA Kit Wako Ⅱ 人淀粉样蛋白抗体(1-40)ELISA试剂盒II |
96wells | for Immunochemistry | – |
| 294-62501 | Human/Rat Beta Amyloid(40)ELISA Kit Wako 人/鼠淀粉样蛋白抗体(40)ELISA试剂盒 |
96wells | for Immunochemistry | – |
| 290-62601 | Human/Rat Beta Amyloid(42)ELISA Kit Wako 人/鼠淀粉样蛋白抗体(42)ELISA试剂盒 |
96wells | for Immunochemistry | – |
| 292-64501 | Human/Rat Beta Amyloid(42) ELISA Kit Wako, High Sensitive 人/鼠淀粉样蛋白抗体(42)高灵敏度ELISA试剂盒 |
96wells | for Immunochemistry | – |
| 294-64701 | Human/Rat Beta Amyloid(40) ELISA Kit II 人/鼠淀粉样蛋白抗体(40)ELISA试剂盒II |
96wells | for Immunochemistry | – |
- 产品特性
- 相关资料
- Q&A
- 参考文献
β-Amyloid ELISA 试剂盒
——定量检测 Aβ40/Aβ42
阿尔茨海默症(Alzheimer's Disease, AD),俗称老年痴呆症,其特征是在大脑神经细胞中存在老年斑(Senile Plaques,SPs) 和神经元纤维缠结(Neuro Fibrillary Tangles, NFT),老年斑的主要组成蛋白是 β- 淀粉样多肽(Amyloid Peptide, Aβ)40 和 42(43),Aβ42 比 Aβ40 更容易发生聚集。因此,蛋白样多肽的聚集开始于 Aβ42 而不是 Aβ40。出现了 Aβ42 而没有出现 Aβ40 是阿 尔茨海默症的早期特征;出现了 Aβ40,尤其是在成熟老年斑的中心部分出现则代表进入阿尔茨海默症的晚期阶段。
本产品可检测与阿尔茨海默病相关的淀粉样蛋白β蛋白质(1-40)以及淀粉样蛋白β蛋白质(1-42)的高灵敏度ELISA试剂盒。与以往试剂盒相比较,检测灵敏度提高约10倍,检测范围在0.1~20.0(pmol/L)。
另外,因为以往产品同样标志抗体Fab’化,非特异性结合降低。由于运用的是武田药品工业株式会社开发的特异性非常高的单克隆抗体,不仅是组织提取液、培养上清液、脑脊髓液,而且以前检测较困难的血浆中Aβ40以及Aβ42亦可高灵敏度检测。
◆优点
● 可检测多种样品类型:脑组织样品,培养基上清样品,脑脊髓液样品, 血浆样品等
● 特异性极强的抗体,避免非特异性结合
BAN50:Aβ肽N末端1-16特异性
BNT77:Aβ11-28特异性
BA27:Aβ40 C末端特异性
BC05:Aβ45 C末端特异性
● 极高的灵敏度,可检测至 pmol 级含量
● 使用此产品的文章已在Science、Biochemistry、Neuron 等多家国际顶尖刊物发表
|
产品 |
Wako 产品 |
A 产品 |
对比优势 |
|
产品名称 |
Human/Rat beta (40) ELISA Kit Wako |
Human 40 ELISA Kit |
|
|
检测原理 |
夹心法 ELISA |
夹心法 ELISA |
|
|
使用的抗体 |
包被的抗体 ,HRP 标记的检测抗体 |
包被的抗体,检测抗体,HRP标记的识别检测抗体的抗体 |
Wako产品检测需 2 个抗体,而A产品需 3 个抗体 |
|
检测物种 |
人,小鼠,大鼠 |
人 |
Wako 产品可检测物种多于A产品 |
|
检测范围 |
1.0~100 pmol/L |
<100 pmol/L |
|
|
检测灵敏度 |
0.25 pmol/L |
1.25pmol/L |
Wako产品灵敏度更高 |
|
检测样品 |
脑组织样品,培养基上清样品,脑脊髓液样 品,血浆样品 |
培养基上清,组织匀浆液,脑脊 髓液 |
|
◆试剂盒构成
|
抗体包被的微平板 1块 标准溶液 2ml×2支 标准稀释液 2ml×2支 清洗液(20x) 50ml×1支 HRP标记抗体溶液 12ml×1支 TMB溶液 12ml×1支 终止液 12ml×1支 密封件 3支 |
 |
① 加入100ul 的标准品和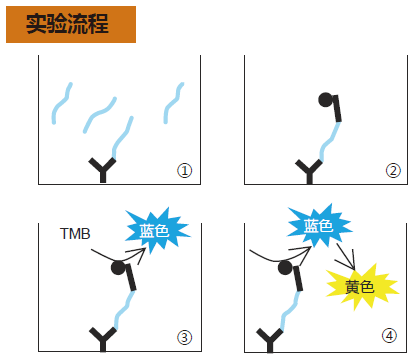 样品,在4 度冰箱中密封过夜。
样品,在4 度冰箱中密封过夜。
↓
② 加入HRP标记的抗体溶液,在4 度冰箱中孵育。
↓
③ 加入100ulTMB 溶液室温孵育30 分钟,避光,密封盖子,进行显色反应。
↓
④ 加入100ul 终止液,测OD450nm值。
◆案例
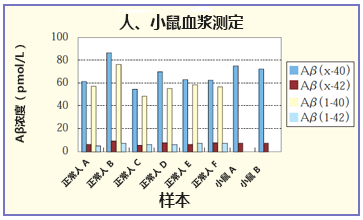
案例1.人、小鼠血浆的测定
使用EDTA2K真空采血管采血,置于5000g、4℃、离心15分钟,分离血浆,使用之前存放于-80℃。
用试剂盒附带的标准稀释液,4倍样本稀释后测定。
(*Aβ(1-40)以及Aβ(x-40)的测定使用人β淀粉样蛋白(1-40)ELISA试剂盒WakoⅡ(产品编号:298-64601)以及人/大鼠β淀粉样蛋白(40)ELISA试剂盒WakoⅡ(产品编号:294-64701)。
案例2.小鼠脑组织的测定
用2mL的Tris盐水提取12月龄APP转基因小鼠(J20)的脑半球,使用之前置于-20℃保存。
用试剂盒附带的标准稀释液,2倍样本稀释后测定。
除了转基因(tg)小鼠,也可测定野生型(wt)小鼠的微量Aβ。
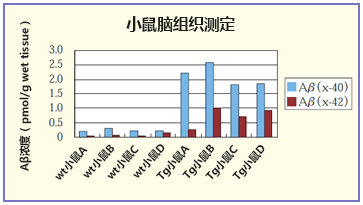
(数据提供:东京大学大学院药学研究科 临床药学教室 岩坪教授 桥本助手)
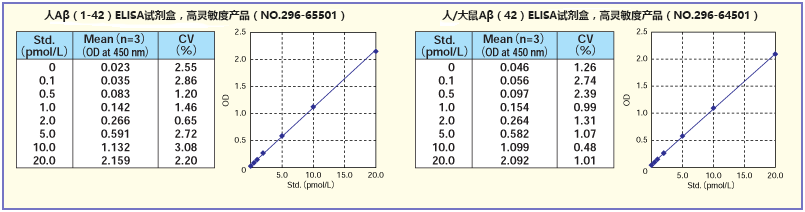
标准曲线
用试剂盒附带的标准溶液制作标准曲线。结果显示,在0.1~20.0(pmol/L)范围内,接近于直线。
添加回收实验
向血浆中分别加入5、10、20(pmol/L),4倍稀释后记录测定时的回收率(%)(测定值/理论值)。基本显示较高的回收率。
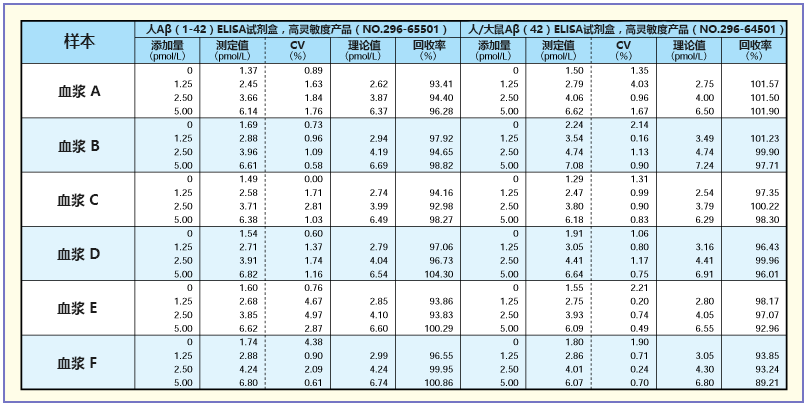
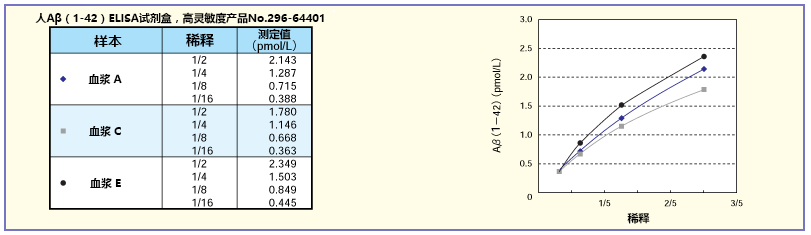
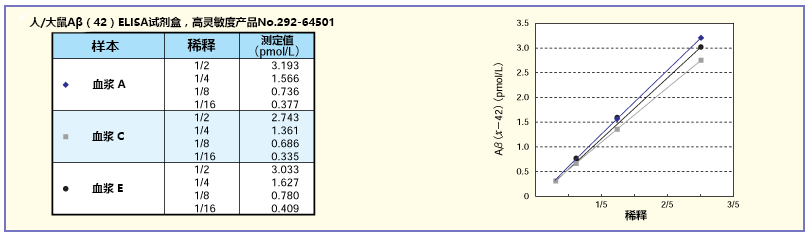
稀释实验
将A、C、E的正常人血浆稀释2~16倍后求稀释曲线。结果显示,特别是人/大鼠系列获得了良好的稀释曲线。
相关资料
|
β-Amyloid ELISA |
阿尔兹海默症相关系列产品 |
常见问题
Q1:标准溶液的OD值低于标准曲线,为什么?
A1:清洗时间是否过长?请将清洗时间控制在2~3分之内结束。另外,请在室温下使用清洗液清洗。在没有培养板
清洗机的情况下,首先将板孔内液体轻轻倒出(注意:此步骤不要污染板孔),用洗瓶将板孔填满清洗液,轻
轻倒出并且反复操作5次。以上步骤的清洗时间要控制在2~3分钟。
Q2:为什么在标准溶液中Aβ肽发生了凝集?
A2:为了让标准溶液不凝集,请在冷藏环境保存即可稳定存在。
Q3:测定值发现存在标准偏差,为什么?
A3:可能是由于在清洗操作过程中板孔中浸水时间(各板孔中装有清洗液时间)的差异而导致测定值产生标准偏
差。特别是利用移液枪手动清洗花费较多时间,可能导致标准偏差较大。请尽可能地在板孔中的浸水时间保
持一致(例:第一回从板右侧开始清洗,第二回从板左侧开始清洗等)
Q4:样本该如何保存?
A4:人体样品(脑组织和脑脊髓液等)需冻存。但是根据样品,即使冻结保存有时测定值也会降低。另外,Aβ浓度
较低时请避免冻结融解。培养上清液请用0.2%牛血清白蛋白、0.075%CHAPS混合后,进行最低限度减少管壁
吸附的损失处理后,冻结保存。
Q5:能测定血清样品吗?
A5:可以测定。但同时采血的血清和血浆相比,血清测定值降低的情况居多(不推荐)。另外,血清冷藏保存后检
测值比血浆更低。
Q6:血浆抗凝固剂使用哪种?
A6:推荐EDTA2K。其他,EDTA2Na和肝素抗凝剂也可以。
Q7:标准的稀释系列浓度不按照以往案例有问题吗?
A7: 没问题。要根据实验情况制定稀释系列。
Q8:标准曲线类型,不是log-log类型,有问题吗?
A8:没问题
Q9:样品推荐n=2以上,但是标准也是n=2吗?
A9:标准也推荐n=2以上,但是样本数多的情况可以选择n=1,根据各自实验情况决定。
Q10:请告知开封试剂的保存方法?
A10:把微孔板整洁地放回到铝袋中,放入干燥剂,冷藏保存即可。
|
产品编号 |
产品名称 |
参考文献引用 |
|
|
298-64601 |
Human β Amyloid(1-40)ELISA Kit Wako Ⅱ |
1 |
Wan W, Zhang C, Danielsen M, et al. EGb761 improves cognitive function and regulates inflammatory responses in the APP/PS1 mouse[J]. Experimental gerontology, 2016, 81: 92-100.<链接> |
|
2 |
Katsuda T, Oki K, Ochiya T. Potential application of extracellular vesicles of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics[M]//Stem Cell Renewal and Cell-Cell Communication. Humana Press, New York, NY, 2014: 171-181.<链接> |
||
|
3 |
Richens J L, Vere K A, Light R A, et al. Practical detection of a definitive biomarker panel for Alzheimer’s disease; comparisons between matched plasma and cerebrospinal fluid[J]. International journal of molecular epidemiology and genetics, 2014, 5(2): 53.<链接> |
||
|
296-64401 |
Human β Amyloid(1-42) ELISA Kit Wako, High Sensitive |
1 |
Richens J L, Spencer H L, Butler M, et al. Rationalising the role of Keratin 9 as a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Scientific reports, 2016, 6.<链接> |
|
2 |
Xie Z, McAuliffe S, Swain C A, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid aβ to tau ratio and postoperative cognitive change[J]. Annals of surgery, 2013, 258(2).<链接> |
||
|
3 |
Richens J L, Vere K A, Light R A, et al. Practical detection of a definitive biomarker panel for Alzheimer’s disease; comparisons between matched plasma and cerebrospinal fluid[J]. International journal of molecular epidemiology and genetics, 2014, 5(2): 53.<链接> |
||
|
4 |
Kim M Y, Kim K N, Cho H M, et al. Reference Intervals for Plasma Amyloid β in Korean Adults Without Cognitive Impairment[J]. Annals of laboratory medicine, 2016, 36(6): 595-598.<链接> |
||
|
5 |
Zhou L, Chan K H, Chu L W, et al. Plasma amyloid-β oligomers level is a biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis[J]. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 2012, 423(4): 697-702.<链接> |
||
|
292-62301 |
Human β Amyloid(1-40) ELISA Kit Wako |
1 |
Bourdenx M, Dovero S, Thiolat M L, et al. Lack of spontaneous age-related brain pathology in Octodon degus: a reappraisal of the model[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7.<链接> |
|
2 |
Waragai M, Moriya M, Nojo T. Decreased N-Acetyl Aspartate/Myo-Inositol Ratio in the Posterior Cingulate Cortex Shown by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy May Be One of the Risk Markers of Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease: A 7-Year Follow-Up Study[J]. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 2017 (Preprint): 1-17.<链接> |
||
|
3 |
Waragai M, Hata S, Suzuki T, et al. Utility of SPM8 plus DARTEL (VSRAD) combined with magnetic resonance spectroscopy as adjunct techniques for screening and predicting dementia due to Alzheimer's disease in clinical practice[J]. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 2014, 41(4): 1207-1222.<链接> |
||
|
298-62401 |
Human β Amyloid(1-42) ELISA Kit Wako |
1 |
Waragai M, Moriya M, Nojo T. Decreased N-Acetyl Aspartate/Myo-Inositol Ratio in the Posterior Cingulate Cortex Shown by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy May Be One of the Risk Markers of Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease: A 7-Year Follow-Up Study[J]. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 2017 (Preprint): 1-17.<链接> |
|
2 |
Brubaker W D, Crane A, Johansson J U, et al. Peripheral complement interactions with amyloid β peptide: Erythrocyte clearance mechanisms[J]. Alzheimer's & Dementia, 2017.<链接> |
||
|
3 |
Crane A, Brubaker W D, Johansson J U, et al. Peripheral complement interactions with amyloid β peptide in Alzheimer's disease: 2. Relationship to Aβ immunotherapy[J]. Alzheimer's & Dementia, 2017.<链接> |
||